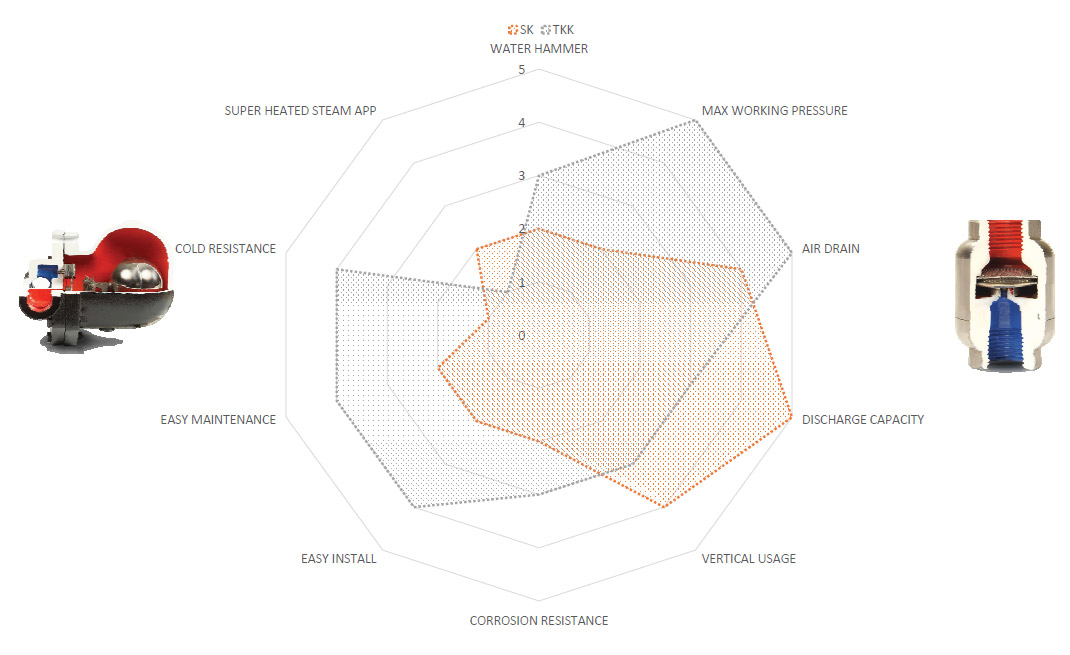
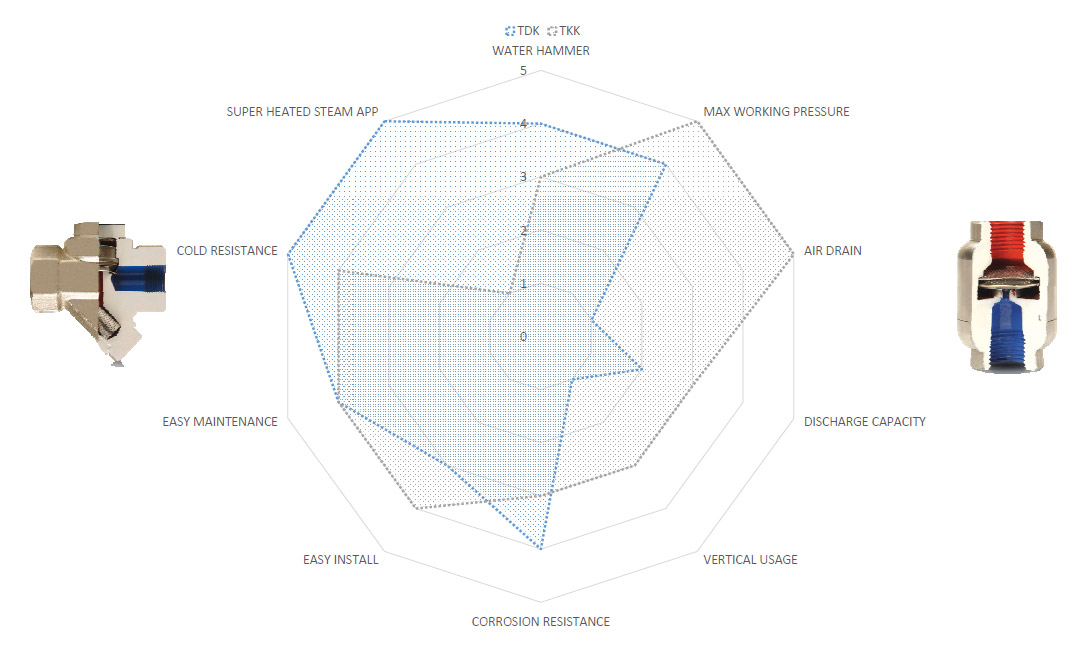
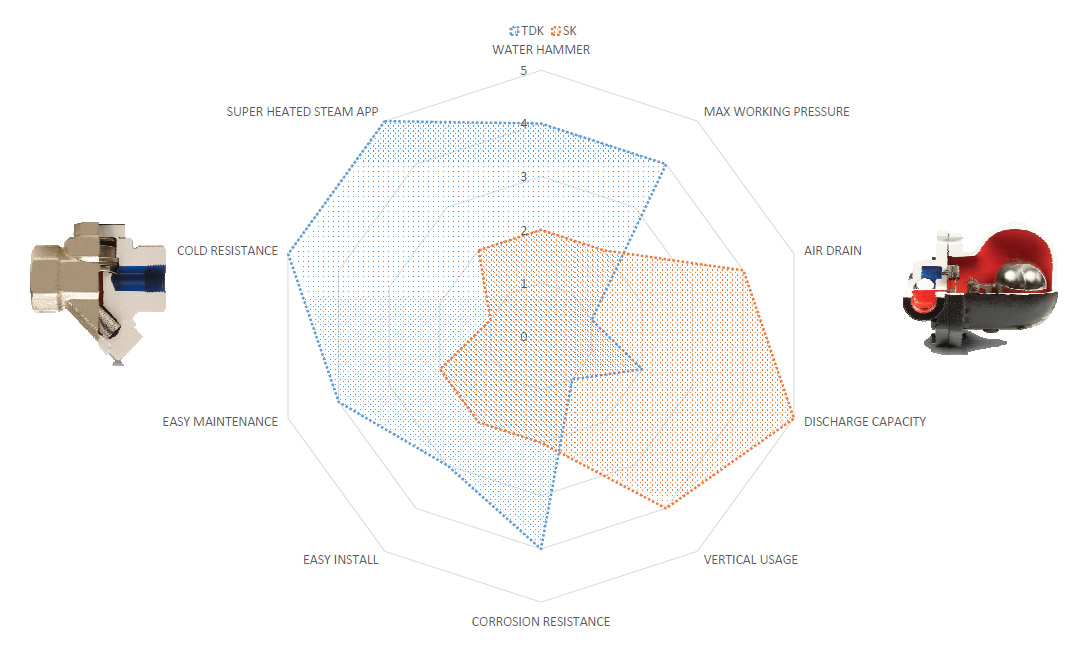
The main criteria for the selection of the type are as follows, although they can not be listed in order of importance since it varies from application.
Resistance to freezing: Trap should resist to freezing for instance outdoor using in cold countries, body of the trap should not broken because on the difference on temperature when t he s team l ine and/or process shout down. For such applications body should not keep condensate. The ideal traps are thermostatic, thermodynamic and bi-metallic. Inverted bucket and float t raps should not install such processes.
Installation versatility: Traps that should install with certain position should be chosen accordingly to the line. For instance thermodynamic steam traps should be installed on the horizontally otherwise they cannot work properly and have less cycle life, float steam traps should be also installed horizontally otherwise they will be failed as either open or blocked/closed all the time.
Air venting: Traps especially for steam line where lots of air rooms and gas occurs should be able to discharge this gas otherwise they will be failed as either open or blocked:/closed all the time.
Resistance to water hammer: Traps especially for steam line where lots of air rooms and gas occurs and becomes a water hammer should be either able to discharge this gas or have strong mechanism that can resist against water hammer otherwise they will be damaged easily.
Discharging capacity: Traps especially for big sized lines such as 1 ½” and 2” should be able to discharge all the condensate that occurs on the process otherwise accumulated condensate can damage the pipe-line and as well to the equipment, plus it will be a result of losing the heat of steam.
Heat Exchange efficiency: traps such as thermostatic types which are discharging the sub cooled condensate do not allow an efficient heat ex change and should not be installed fo r super-heated steam lines. Otherwise they will be blocked immediately and cause lots of important problems such as damaging turbines.
Sensitivity to back pressure: Traps such as thermodynamic types should not be installed on steam lines where the back is more than 80 % of inlet pressure. In such cases thermodynamic traps failed as either open or blocked / closed all the time.
Resistance to corrosive conditions: The initial parts of all traps should be stainless steel but for such cases where even the outer conditions are corrosive traps should have stainless steel body and cover as well.
| Trap Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Thermostatic | - Easy maintenance - Spare parts available - Installation in every position - Long service life - Works under back pressure more than 80% inlet pressure - Easy to clean the filter - Air venting - Resists to water hammer - Resists to corrosion - Resists to freezing - Slim and light - Built-in screen - Easy replaceable seat and capsule |
- Not suitable for super-heated steam |
| Thermodynamic | - Installations at super-heated steam - Easy to clean the filter - Resist to water hammer - Resist the corrosion - Resist the freezing - Spare parts available - Built-in screen - Low cost, easy maintenance - Fixed orifice |
- Installation only horizontally |
| Bi-Metallic | - Installation at super-heated steam - Easy to clean the filter - Resist to water hammer - Resists the corrosion - Resist the freezing - Spare parts available - Acting as non-return valve - Energy saving - Works under back pressure - Installation in every position |
- Difficult maintenance |
| Float Type | - Installation both horizontal and vertical - High discharge capacity - Air venting - Can use at different ΔP applications |
- Installation both horizontal and vertical |
| Inverted Bucket | - Strong structure - Resistant against water hammer |
- Difficult maintenance |
ORIFICE SIZE AND WORKING PRESSURE RELATION
To lift the float for discharging the condensate from the orifice hole; lifting force of the condensate must be higher than the force wich is created by the pressure that effects to the A area. Lever are size of float type steam traps(LS) are standard. Buoyancy of water(FW) is also fixed according to weight of ball. For easy explanation:
If; FWx LS=100;
FW x LS > PS x AO
100>4,5x AO1 (AO1 = 22,2)
100>10x AO2 (AO2 = 10)
100>14x AO3 (AO3 = 7,14)
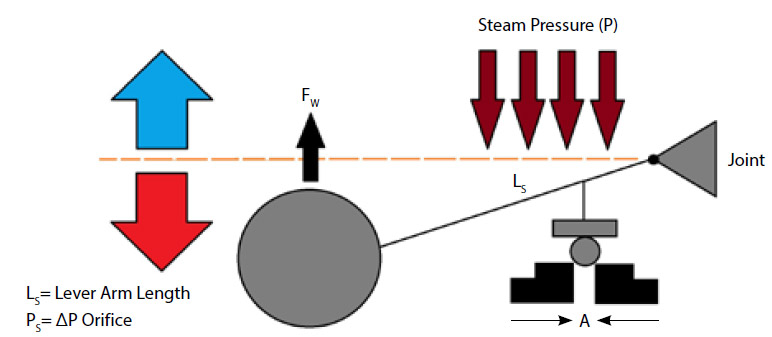
Comparison of Steam Traps