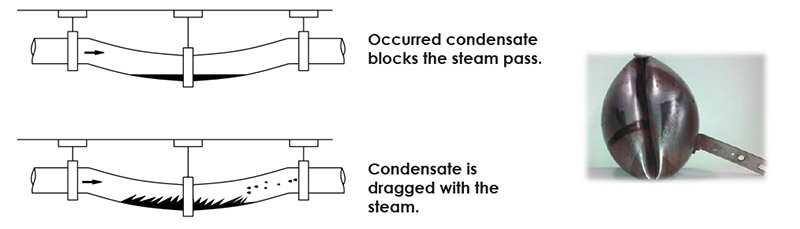
Water Hammering
In the pipelines where condensate collecting is permissible, steam drags the condensate, this condensate damages the Gasketcted armatures like valves, filters or steam traps. Movement of the occurred condensate by steam is called water hammering. Water hammering may cause serious damages to the armatures in the system. In order to prevent this, water in the system must be drained.
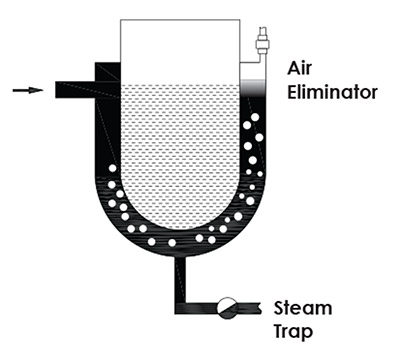
Air Elimination
The steam in the system cools down in time and becomes condensate. Pressure drops and vacuum occurs, this results with air to get in the system from flange gaskets or other
connection areas. Some air with the steam also enters the system. The air in the machine is compressed by the steam in the machine and may lock the steam trap. Because of that, air in the system must be eliminated by an air eliminator. In such cases, steam traps with air and gas ventilation function are suggested.
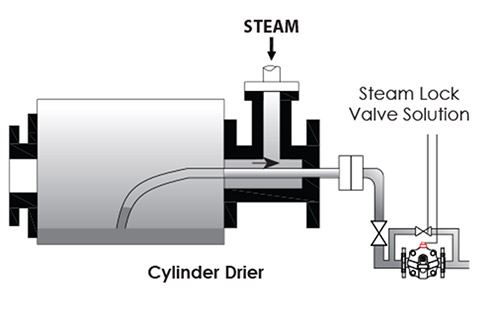
Steam Lock
Usually, the steam to get inside the steam trap by an un-desired way in cylinder drier units is called steam lock. As the drier cylinder rotates in a constant speed, the steam gets inside the cylinder condensates, sometimes this condensate reaches the steam trap passing through the pipe and makes steam trap to remain as closed. That may cause a problem like the condensate can’t be discharged because of the closed steam trap. This may be solved by a built-in steam lock mechanism valve or the by-pass valve to be opened as to be in quarter position. As the steam starts to be taken out by these valves, flow re-starts and condensate rises through the pipe to get inside the steam trap to be discarged.
CONDENSATE DISCHARGE FROM MAIN LINES
Because of the low energy loss and low costs, thermodynamic steam traps are preferred in main lines. In order to drag down the condensate, steam lines must be constructed with an angle as it is seen below.
The points where the main lines are elevated, condensate collecting pockets should be created at the bottom turning points and thermodynamic steam traps to be placed.
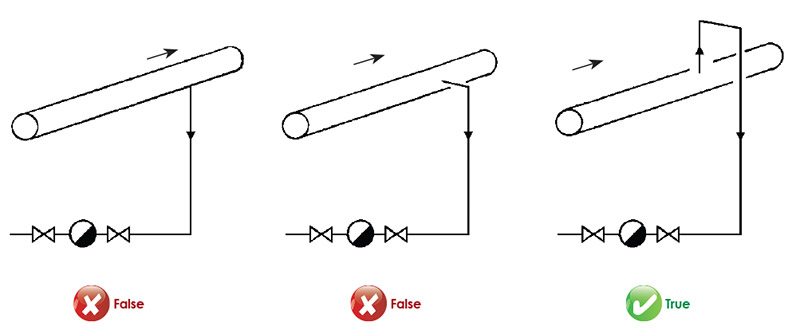
Branch lines to the steam equipment should not be taken from the bottom or side walls of the main lines because of the formation of dirt or residues. Branch lines should always be taken from the top of the main steam lines.
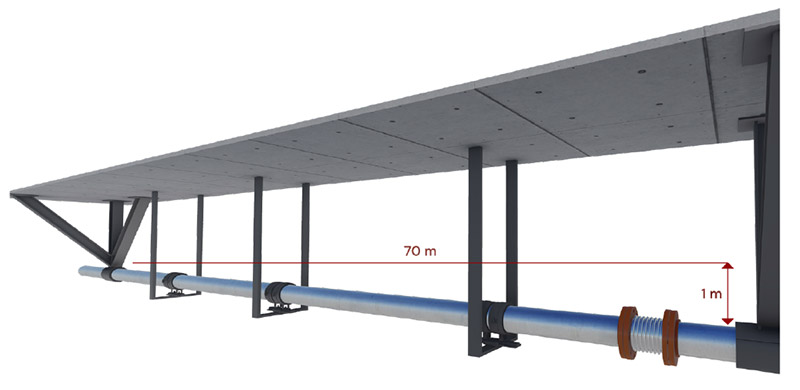
If any elevation in the pipeline after the boiler is applicable, the pipeline diameter of the elevated area is built bigger. That helps to reduce the speed of the condensate and flows back to the discharge unit. In elevating parts of the pipelines, creating condensate discharge units in every 15 meters is advised.
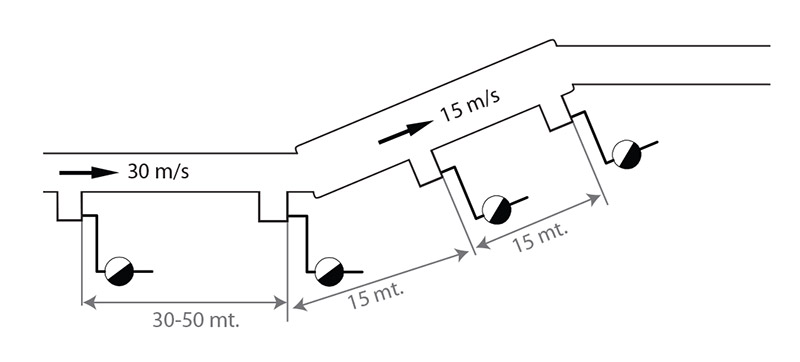
Condensate discharge unit should be placed in main steam lines in every 50 meters if the line is indoor and insulated or in every 30 meters if the line is outdoor and insulated. If any equipment like pressure reducer, pressure holder or proportional valve is installed in the line, a condensate discharge unit must be placed before these equipment.
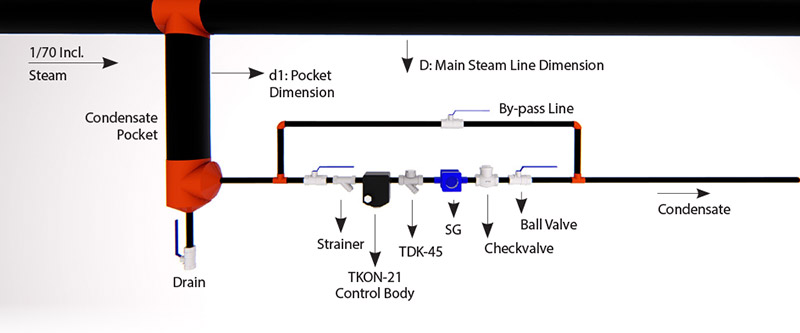
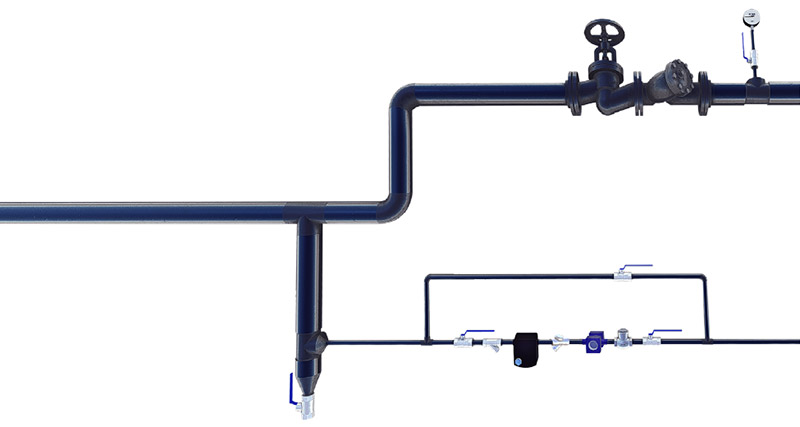
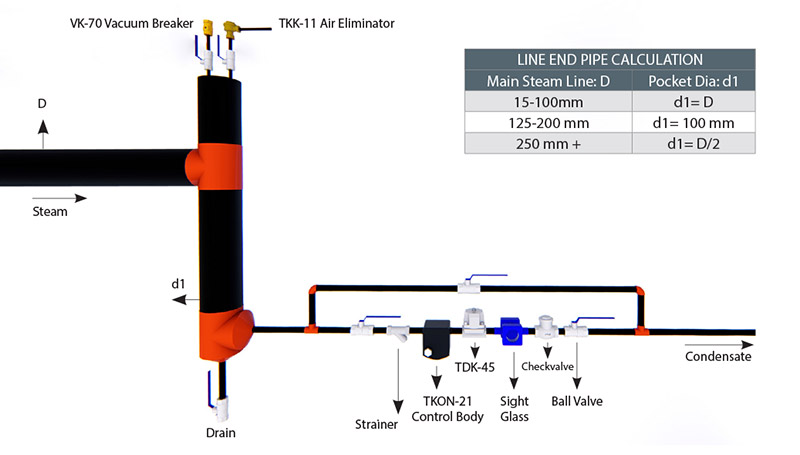
The occurred air and condensate around connection areas in the pipelines are dragged to the end of the line. If that air and condensate are not discharged, they may block the steam flow. In such cases, formed air and condensate are discharged with a line end application shown below. The steam trap kind must be thermodynamic.
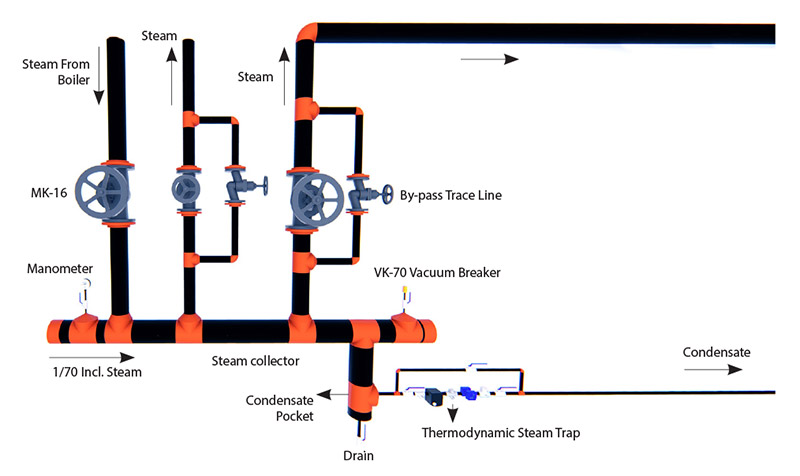
The system that distributes steam is called “collector”. Steam condensates in the collectors. The condensate is usually charged by thermodynamic steam traps from the collectors.
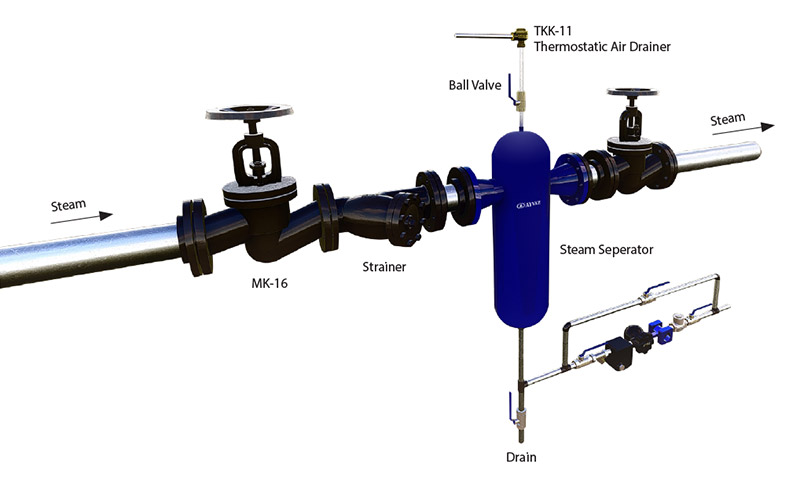
In cases where dry and clean steam is required, branch line should be connected to the machine and process with a steam separator. This will help to collect the water at the bottom of the separator and to be discharged from the steam trap.