Under a certain pressure, heated water’s temperature and enthalpy is increased. This continues until the boiling point of the water. At this point, temperature of the water remains same as all the water turns in to steam. After this, in order to benefit from the heat of the steam, steam is trapped. The condensate which is in Gasketct with steam is at the steam temperature. When discharged condensate by steam trap gets in a lower pressure ambient, condensate cools down to the saturated temperature of the ambient pressure and some of it gets evaporated because of the temperature difference.
The outcome energy causes some of the condensate to get evaporated, the steam which is the result of this evaporation is called “flash steam”. In another word, the steam which is the result of the movement of condensate from high temperature and high pressure ambient to low pressure ambient.
Important points of gathering flash steam;
1- For minimum amount of flash steam, huge condensate amount is required. Steam trap capacities should be selected carefully. Closing of the control valves provide pressure drop to the system, this should be estimated.
2- Application area should be appropriate for flash steam use, flash steam consumption should be equal or above flash steam amount.
3- Use of flash steam must be close to outlet of the high temperature condensate. Transport of low pressure condensate requires high diameters of pipeline and increases invest costs.
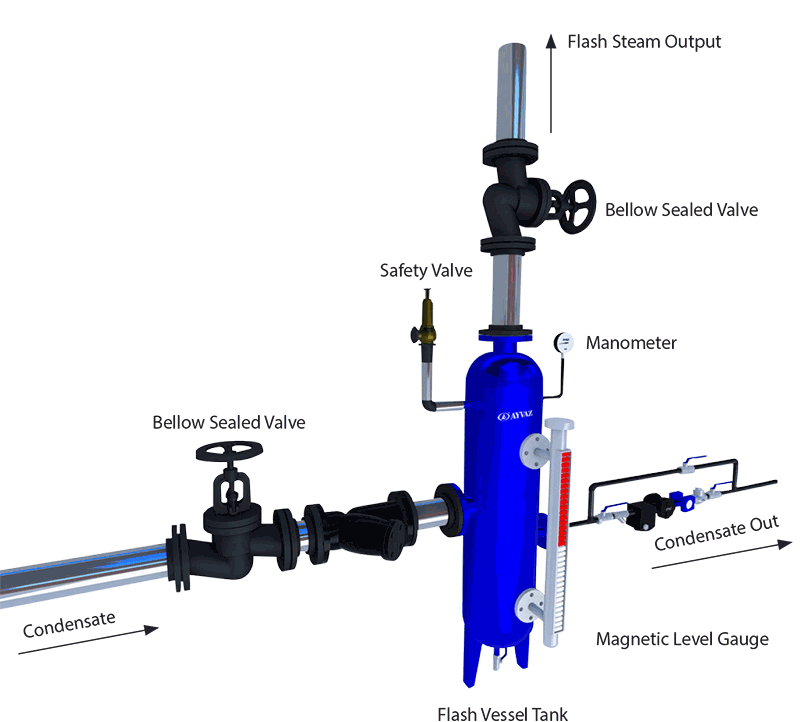
Flash steam armatures and tanks can be seen below,
Calculation of flash steam amount:
Ch: Sensible heat in the condensate at the higher pressure before discharge (kj/kg)
Cl: Sensible heat in the steam at the condensate at the lover pressure after discharge takes place (kj/ kg)
Lh: Latent heat in the steam at the lower pressure to which the condensate has been discharge (kj/kg)
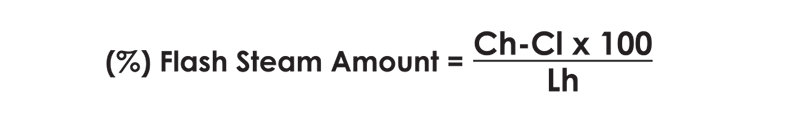
As a result, as the pressure difference increases, flash steam amount is also increases. Also, steam trap type is also affective on the flash steam amount. Mechanical steam traps discharge close to the saturated temperature. Meanwhile, thermostatic discharge lower than saturated temperature and the flash steam amount is lower accordingly. The amount of generated flash steam is lower because they are drained under the traps vaporization temperature.
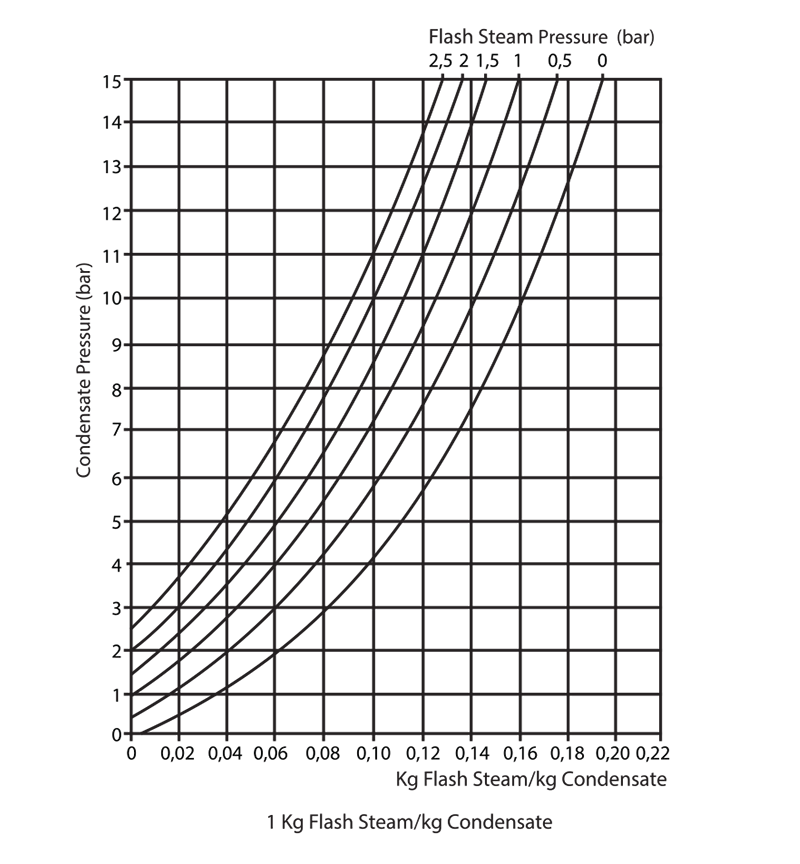
Example 1:
If the discharge of the same system is done by AYVAZ TKK-2Y thermostatic steam trap with 10K and 30K capsule options.
Condensate temperature for 10 K:
170.5 – 10 = 160.5 °C
Condensate temperature for 30 K :
170.5 - 30= 139.5 °C
From the saturated steam table, enthalpies for these temperatures are;
For 10 k: 678.2 kj/kg
For 30 k: 593.3 kj/kg.
Example 2:
Calculation of the flash steam amount for below system
From the saturated steam table;
At 8 bar, 170.5 °C, enthalpy of condensate = 720.94 kj/kg
At 1 bar, 100.0 °C, enthalpy of condensate = 419.00 kj/kg
Difference of enthalpy is 301.94 kj/kg.
Hidden heat of the water vaporized at 1 bar is:
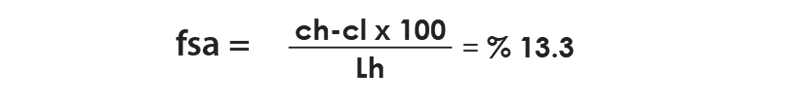
If steam consumption of the system is 1000 kg, flash steam amount is 133 kg.
At 1 bar, 100.0 °C, enthalpy of condensate = 419.00 kj/kg. Difference enthalpies are;
10 K: 678.2-419.0 = 252.2 kj/kg
30 K: 593.3-419.0 = 174.3 kj/kg
Hidden heat of the water vaporized at 1 bar is LH =2.257 kj/kg. So, the flash steam amounts are;
For 10 K, FSA (292.2 / 2257).100 = % 11.48
For 30 K, FSA (174.3 / 2257).100 = % 7.72
If steam consumption of the system is 1000 kg, flash steam amounts are;
For 10 K: 114.8 kg
For 30 K: 77.2 kg
As it is seen in the above examples, thermostatic steam traps provide less flash steam than mechanical and thermodynamic steam traps. In abroad meaning, thermostatic steam traps are the most efficient steam traps in the manner of “Energy Saving”. This is the main reason that this type of steam traps are preferred especially for the tracing lines and heating equipment at petrol refineries.
Also, Just because Ayvaz thermostatic capsule has 3 different options as 5K, 10K, 30K , it provides optimum efficiency advantage in relation with request and operation conditions. It is also used especially tyre production.
The diameter of the flash steam tank should be a diameter that allows the passage of the condensate without coming into turbulence.
If the difference between high and low pressure is small.
The amount of steam is less than the amount of condensate. Flash steam outlet pipe selecting the diameter according to the speed will cause the tank to remain small in which case the tank must be selected to be two diameters larger.
Choosing Flash Vessel
1- Maximum condensation amount is required to obtain maximum flash steam. For this reason, the capacity of steam traps must be selected carefully, taking into consideration the counterpressure. It should also be noted that in systems where temperature control valves are used, the valve will be closed and the pressure will drop.
2- The amount of use of flash steam systems must be equal to the amount of flash steam. Steam can be provided by pressure drop from a higher pressure steam line when the flash steam is missing. If flash steam is excessive, some of the flash steam must be thrown out. Also, since the flash used in heating will not be needed in summer, a heat recovery system will not be necessary. Therefore, the amount of flash steam required must be prepared.
3- It is beneficial if the system to be used with flash steam is close to the outlet of the condensate at high pressure. The transport of low-pressure condensate requires large diameters and will increase investment costs. In addition, the heat losses that will occur on large pipe diameters will reduce the benefits of flash buckets.

